瀑布流
大约 2 分钟
瀑布流
布局和实现逻辑
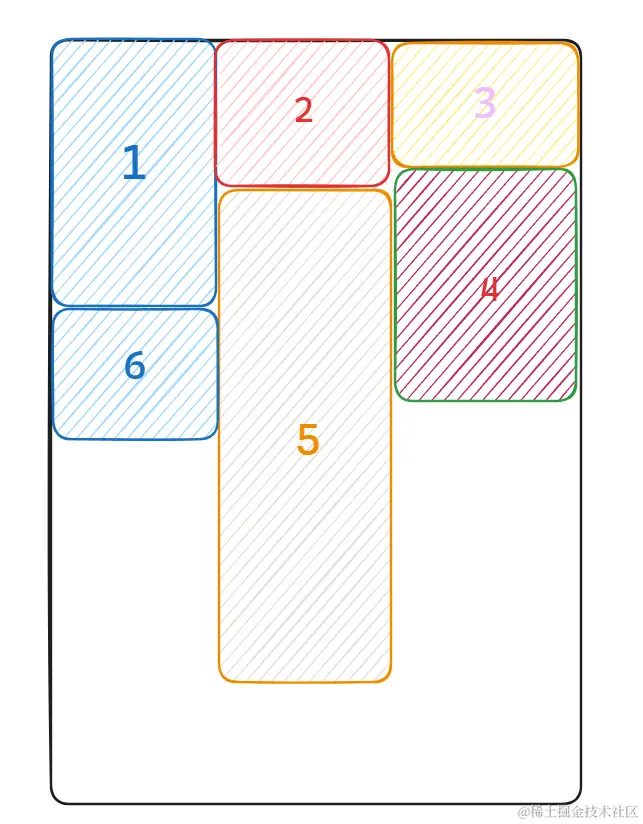
- 首选确定列数, 列数和屏幕宽度有关
- 维护一个数组(长度为列数),第一行依次排列(各列放入数组中),第二列选择第一行中高度最小的列,并将第二行的高度加入对应列,以此类推
<template>
<div class="fs-waterfall-container" ref="containerRef">
<div class="fs-waterfall-list">
<div
class="fs-waterfall-item"
v-for="(item, index) in state.cardList"
:key="item.id"
:style="{
width: `${state.cardPos[index].width}px`,
height: `${state.cardPos[index].height}px`,
transform: `translate3d(${state.cardPos[index].x}px, ${state.cardPos[index].y}px, 0)`,
}"
>
<slot name="item" :item="item" :index="index"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
.fs-waterfall {
&-container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow-y: scroll; // 注意需要提前设置展示滚动条,如果等数据展示再出现滚动造成计算偏差
overflow-x: hidden;
}
&-list {
width: 100%;
position: relative;
}
&-item {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
}
- container 需要滚动,list 需要相对定位,item 需要绝对定位
- 确定瀑布流的常量
- 列数(column)
- 列间距(gap)
- 距底距离(bottom)
图片的宽高
- 项目中使用会由后端和图片地址一同返回
- 前端计算(预加载),需要加载所有图片后才能渲染图片
function preLoadImage(link) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { const img = new Image() img.src = link img.onload = () => { // load 事件代表图片已经加载完毕,通过该回调才访问到图片真正的尺寸信息 resolve({ width: img.width, height: img.height }) } img.onerror = err => { reject(err) } }) }
卡片的宽度
卡片的宽度和浏览器宽度相关
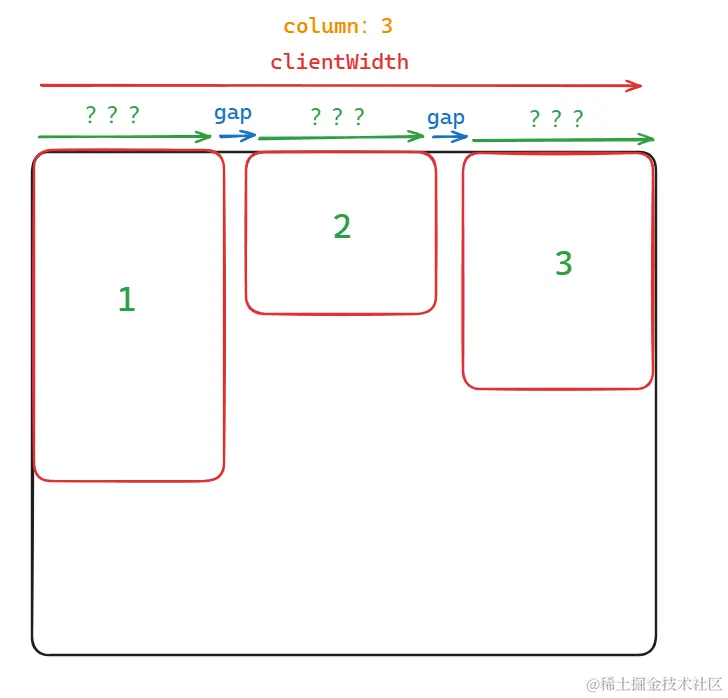
const containerWidth = containerRef.value.clientWidth; state.cardWidth = (containerWidth - props.gap \* (props.column - 1)) / props.column; ```
计算最小列高度和卡片位置
const minColumn = computed(() => {
let minIndex = -1,
minHeight = Infinity
state.columnHeight.forEach((item, index) => {
//columnHeight为维护的列高数组
if (item < minHeight) {
minHeight = item
minIndex = index
}
})
return {
minIndex,
minHeight,
}
})
- 遍历数据项,计算当前数据项缩放后的卡片高度(根据后端返回的宽高信息以及 state.cardWidth 计算)
- 区分第一行和其余行布局
- 第一行卡片位置信息紧挨排布,高度更新至对应列的 state.columnHeight 中
- 其余行需要先获得最小高度列信息再计算其卡片位置,最终将高度累加到对应列的 state.columnHeight 中
// 计算卡片位置
const computedCardPos = (list: ICardItem[]) => {
//为图片数组
list.forEach((item, index) => {
const cardHeight = Math.floor((item.height * state.cardWidth) / item.width)
if (index < props.column) {
state.cardPos.push({
width: state.cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
x: index % props.column !== 0 ? index * (state.cardWidth + props.gap) : 0,
y: 0,
})
state.columnHeight[index] = cardHeight + props.gap
} else {
const { minIndex, minHeight } = minColumn.value
state.cardPos.push({
width: state.cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
x: minIndex % props.column !== 0 ? minIndex * (state.cardWidth + props.gap) : 0,
y: minHeight,
})
state.columnHeight[minIndex] += cardHeight + props.gap
}
})
}